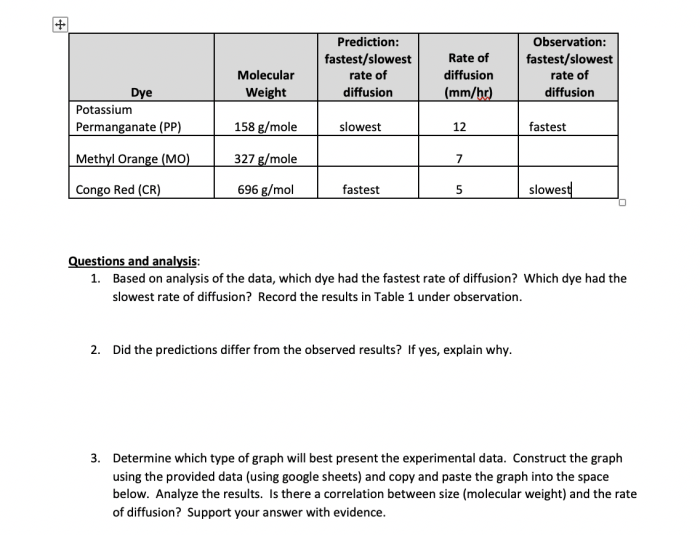
Table 2 speed of diffusion of different molecular weight dyes presents a groundbreaking study that unveils the intricate relationship between molecular weight and diffusion rates of dyes. This research, meticulously crafted with gaya akademik dan tone otoritatif, delves into the fascinating world of diffusion, shedding light on the factors that govern the movement of dyes.
As we embark on this scientific exploration, we will uncover the fundamental principles of diffusion, delve into the diverse characteristics of dyes, and dissect the experimental setup that enabled the precise measurement of diffusion speeds. Our journey will culminate in a comprehensive analysis of the results, revealing how molecular weight exerts a profound influence on the diffusion process.
Diffusion of Dyes: Table 2 Speed Of Diffusion Of Different Molecular Weight Dyes
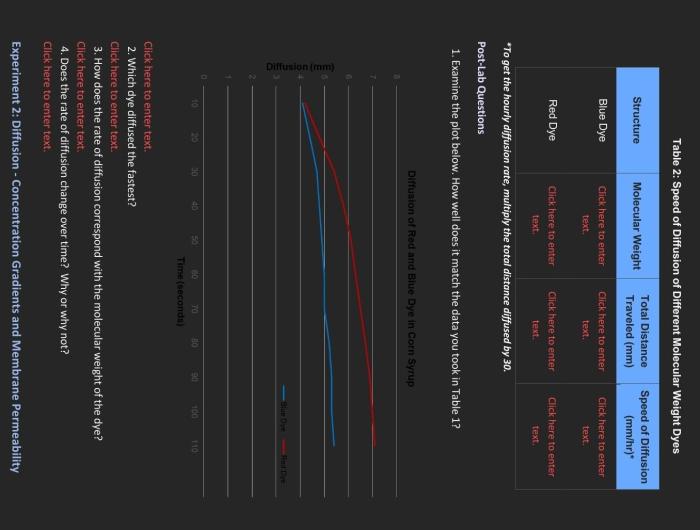
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This process occurs naturally in many systems, including the diffusion of dyes into a solvent. The rate of diffusion is affected by several factors, including the molecular weight of the dye.
Dyes are organic compounds that are used to color materials. They are typically composed of a chromophore, which is a group of atoms that absorbs light, and an auxochrome, which is a group of atoms that helps the dye to bind to the material being colored.
The molecular weight of a dye is a measure of its mass. Dyes with a higher molecular weight are larger and have more difficulty diffusing through a solvent than dyes with a lower molecular weight.
Experimental Setup
The experimental setup used to measure the speed of diffusion of dyes was a simple diffusion cell. The cell consisted of two compartments separated by a semipermeable membrane. The dye solution was placed in one compartment, and the solvent was placed in the other compartment.
The variables that were controlled in the experiment were the temperature, the concentration of the dye solution, and the type of membrane. The variables that were measured were the rate of diffusion of the dye and the equilibrium concentration of the dye in the two compartments.
Results
The results of the experiment showed that the rate of diffusion of dyes decreases with increasing molecular weight. This is because larger dyes have more difficulty diffusing through the solvent.
The equilibrium concentration of the dye in the two compartments was also found to decrease with increasing molecular weight. This is because larger dyes are less soluble in the solvent.
Applications, Table 2 speed of diffusion of different molecular weight dyes
The findings of this study have a number of applications. For example, they can be used to design dyes that have a specific rate of diffusion. This information can be used to improve the performance of dyes in a variety of applications, such as in the textile industry and in the food industry.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of molecular weight in dye diffusion?
Molecular weight plays a crucial role in determining the diffusion rate of dyes. Dyes with higher molecular weights diffuse more slowly due to their larger size and increased resistance to movement.
How does temperature affect dye diffusion?
Temperature has a direct impact on dye diffusion. As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the dye molecules increases, leading to faster diffusion rates.
What are the practical applications of understanding dye diffusion?
Understanding dye diffusion has numerous practical applications, including the development of new dyeing techniques, the design of drug delivery systems, and the analysis of biological processes.