Unit 3 land based empires 1450 to 1750 – Unit 3: Land-Based Empires (1450-1750) embarks on an exploration of the rise and impact of land-based empires during this transformative period, delving into their territorial expansion, economic consequences, cultural exchanges, political structures, and military advancements.
This comprehensive overview unravels the intricate tapestry of these empires, shedding light on their profound influence and the lasting legacies they left on the world stage.
Territorial Expansion of Land-Based Empires
The period between 1450 and 1750 witnessed significant territorial expansion by land-based empires. This expansion was driven by a combination of factors, including political ambition, economic necessity, and technological advancements.
Key Factors Driving Territorial Expansion
- Political Ambition:Rulers sought to increase their power and prestige by conquering new territories and expanding their empires.
- Economic Necessity:Empires needed to acquire new resources, such as land, labor, and raw materials, to support their growing populations and economies.
- Technological Advancements:Innovations in weaponry, transportation, and communication made it easier for empires to conquer and control distant lands.
Examples of Land-Based Empires with Significant Territorial Growth
- Ottoman Empire:Expanded from Anatolia into the Balkans, Middle East, and North Africa.
- Safavid Empire:Conquered Persia and parts of Mesopotamia, the Caucasus, and Central Asia.
- Mughal Empire:Established in India, expanded to control most of the Indian subcontinent.
- Qing Dynasty:Expanded the Manchu Empire to include China, Tibet, Mongolia, and parts of Central Asia.
Methods of Territorial Expansion
- Military Conquest:Empires used their armies to conquer and annex new territories.
- Diplomatic Alliances:Empires formed alliances with local rulers to gain access to new lands.
- Trade and Commerce:Empires established trading posts and colonies in new territories to gain economic control and influence.
Economic Impact of Land-Based Empires
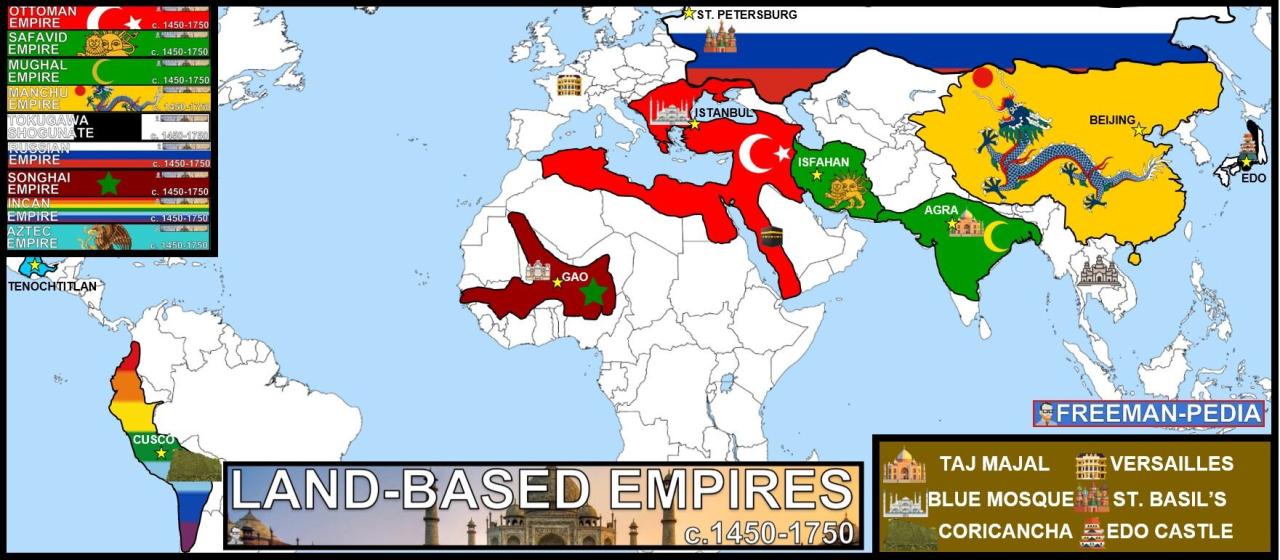
Land-based empires had a profound economic impact on their conquered territories. These empires implemented various economic policies and practices that affected the economies of the regions they controlled.
Economic Policies and Practices, Unit 3 land based empires 1450 to 1750
- Taxation:Empires imposed taxes on conquered territories to generate revenue for their own use.
- Land Redistribution:Empires often redistributed land to their supporters and loyalists, disrupting local economies.
- Trade Monopolies:Empires established trade monopolies to control the flow of goods and extract profits.
Economic Benefits and Challenges
Benefits:
- Increased Trade:Empires facilitated trade between different regions, leading to economic growth and prosperity.
- New Technologies:Empires introduced new technologies and agricultural practices to conquered territories, improving productivity.
- Economic Integration:Empires created larger economic markets, allowing for specialization and increased efficiency.
Challenges:
- Exploitation:Empires often exploited conquered territories for their own economic gain, leading to resentment and resistance.
- Disruption of Local Economies:Empire policies could disrupt local economies, leading to unemployment and poverty.
- Dependence:Conquered territories became dependent on empires for trade and economic support, making them vulnerable to exploitation.
Cultural Exchange and Influence

Land-based empires played a significant role in cultural exchange and influence. The cultures of these empires shaped the cultures of the conquered regions, leading to the emergence of new and hybrid cultural forms.
Ways in which Empire Cultures Shaped Conquered Regions
- Religion:Empires often spread their own religions to conquered territories, influencing local beliefs and practices.
- Language:The languages of empires became the official languages of conquered territories, facilitating communication and administration.
- Art and Architecture:Empire art and architectural styles influenced local art forms, leading to the development of new artistic traditions.
Specific Examples of Cultural Influences and Exchanges
- Ottoman Empire:Introduced Islamic architecture, art, and music to the Balkans and Middle East.
- Safavid Empire:Spread Shia Islam to Persia and influenced the development of Persian art and literature.
- Mughal Empire:Combined Islamic, Hindu, and Persian cultural elements to create a unique Indian-Islamic culture.
Political Structures and Administration: Unit 3 Land Based Empires 1450 To 1750
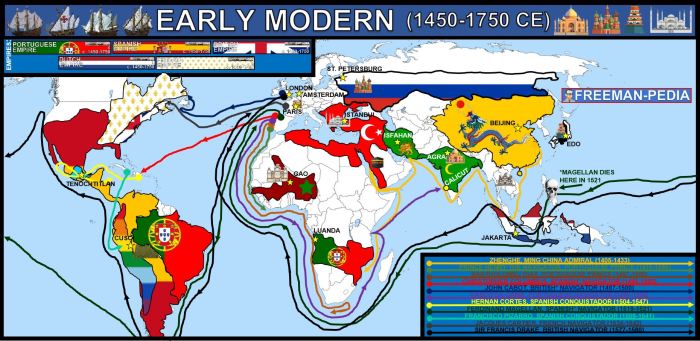
Land-based empires established political structures and administrative systems to govern their conquered territories. These systems varied in effectiveness and legitimacy, depending on the empire and the specific context.
Types of Political Structures
- Direct Rule:Empires appointed governors or viceroys to directly administer conquered territories.
- Indirect Rule:Empires allowed local rulers to retain some authority, while maintaining overall control.
- Colonial Administration:Empires established colonies and implemented their own laws and institutions.
Challenges in Governing Large and Diverse Territories
- Cultural and Religious Diversity:Empires faced challenges in governing territories with diverse cultures and religions.
- Communication and Transportation:Governing large and distant territories required efficient communication and transportation systems.
- Local Resistance:Empires often encountered resistance from local populations, who resented their rule.
Examples of Effective and Ineffective Political Systems
Effective:
- Mughal Empire:Implemented a centralized administration and granted religious tolerance, leading to stability and prosperity.
- Ottoman Empire:Developed a sophisticated bureaucracy and military system, allowing for effective control over its vast territories.
Ineffective:
- Safavid Empire:Faced internal conflicts and Shia-Sunni tensions, leading to political instability and economic decline.
- Qing Dynasty:Struggled to govern its vast territories effectively, leading to regional rebellions and ethnic conflicts.
Military Strategies and Technologies
Land-based empires employed a variety of military strategies and technologies to conquer and defend their territories. These strategies and technologies evolved over time, giving some empires a significant advantage over their rivals.
Military Strategies
- Cavalry Warfare:Empires relied heavily on cavalry for mobility and shock tactics.
- Infantry Tactics:Empires developed infantry formations and tactics to counter cavalry charges and siege fortifications.
- Artillery:Empires used artillery to bombard enemy positions and fortifications, increasing their effectiveness in sieges.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Military Tactics and Weapons
Advantages:
- Cavalry:Cavalry provided speed, mobility, and shock power, allowing empires to outmaneuver and defeat their opponents.
- Infantry:Infantry formations provided stability and defensive power, making them effective in holding positions and repelling attacks.
- Artillery:Artillery allowed empires to bombard enemy positions from a distance, reducing casualties and increasing their chances of victory.
Disadvantages:
- Cavalry:Cavalry was vulnerable to infantry attacks and could be difficult to control in close combat.
- Infantry:Infantry formations were slow and cumbersome, making them vulnerable to cavalry charges and artillery fire.
- Artillery:Artillery was expensive and difficult to transport, limiting its use in certain situations.
Significant Battles and Campaigns
- Battle of Lepanto (1571):A naval battle in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by a coalition of Christian forces, halting its expansion into Europe.
- Battle of Panipat (1556):A decisive battle in which the Mughal Empire defeated the Afghan Suri Dynasty, establishing Mughal dominance in India.
- Siege of Vienna (1683):A failed Ottoman siege of Vienna, marking the beginning of the decline of Ottoman power in Europe.
Answers to Common Questions
What were the primary motivations for the territorial expansion of land-based empires?
Ambitions for wealth, power, and prestige, as well as strategic considerations and the desire to secure access to resources and trade routes.
How did land-based empires influence the economic development of conquered territories?
They introduced new crops, technologies, and economic systems, leading to both economic growth and exploitation in some cases.
What were the key features of the political structures established by land-based empires?
Centralized governance, hierarchical administrative systems, and varying degrees of local autonomy, often shaped by pre-existing political structures.